Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system and is the fifth planet from the sun. It is a gas giant and has a diameter of about 86,881 miles (139,822 kilometers). Here’s a detailed look at Jupiter, its characteristics, and its place in the solar system:

Discovery and Naming:
Jupiter has been known to humans since ancient times. The Babylonians observed the planet and called it Marduk. The Romans named it Jupiter after their god of the same name.
Characteristics:
Jupiter is a gas giant, which means it does not have a solid surface. Its atmosphere is made up mostly of hydrogen and helium, with small amounts of other elements. Jupiter’s strong gravitational field causes its atmosphere to be compressed to high densities.
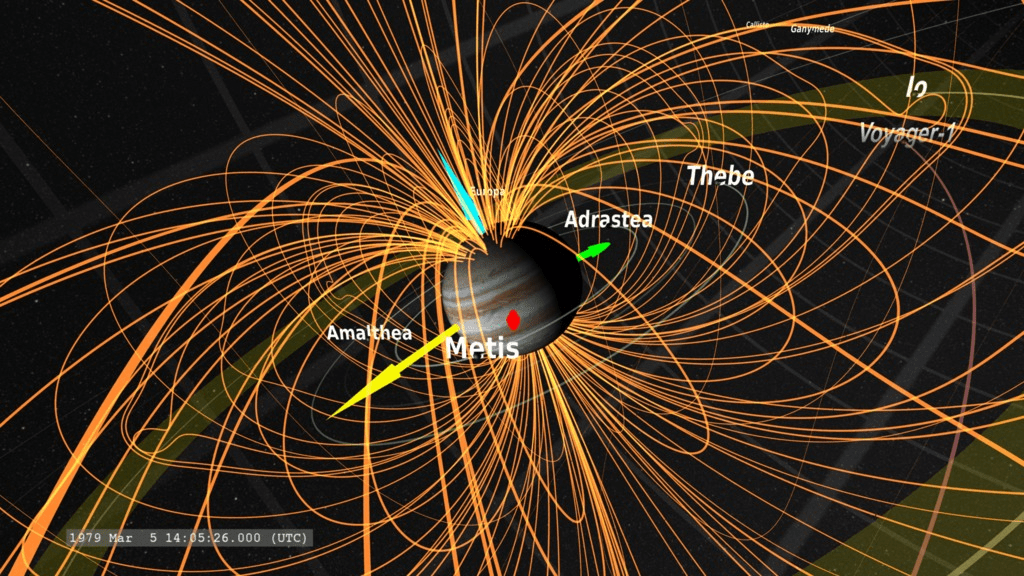
Jupiter has a powerful magnetic field that is about 20,000 times stronger than Earth’s. This field traps particles from the solar wind, which creates the planet’s extensive system of radiation belts. These belts can be hazardous to spacecraft, including the Juno mission, which is currently in orbit around Jupiter.
Moons:
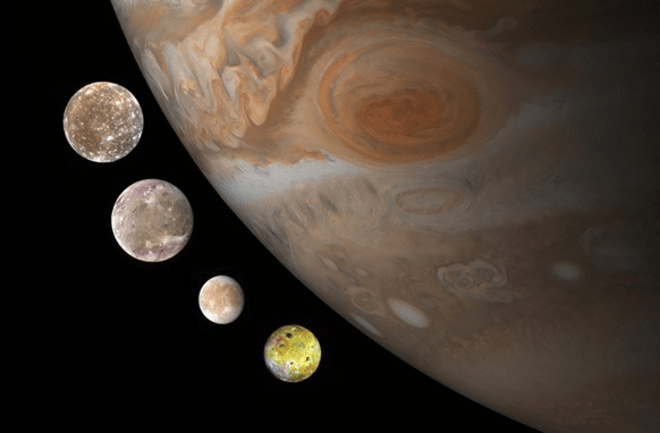
Jupiter has 79 known moons, the largest of which are called the Galilean moons. These moons were discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610 and are named Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. Ganymede is the largest moon in the solar system, and all four of the Galilean moons are larger than Pluto.
Rings:
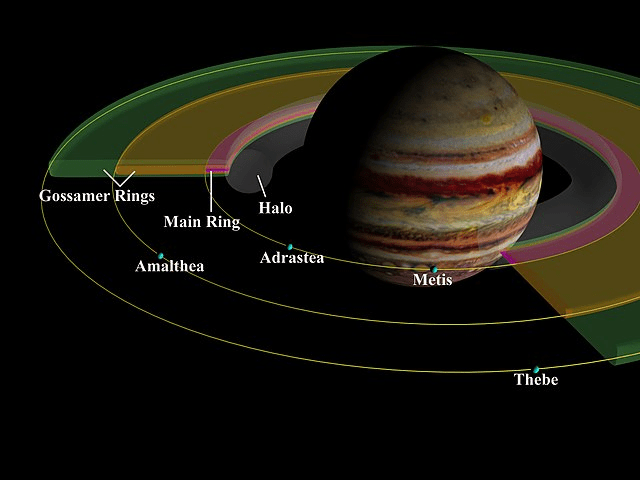
Jupiter has a faint ring system, which was discovered in 1979 by the Voyager 1 spacecraft. The ring system is composed of four main parts: the halo, the main ring, the Amalthea gossamer ring, and the Thebe gossamer ring. The rings are thought to be made up of dust and small particles, and they are not as prominent as the rings of Saturn.
Exploration:
Jupiter has been visited by several spacecraft, including Pioneer 10 and 11, Voyager 1 and 2, Galileo, Cassini-Huygens, New Horizons, and Juno. These missions have provided a wealth of information about the planet’s atmosphere, magnetic field, moons, and rings.
Significance:
Jupiter plays a significant role in the solar system, as its strong gravitational field has helped to shape the orbits of the other planets. It also helps to protect the inner solar system from asteroids and comets, as its gravity can deflect these objects away from the sun.
Physical Characteristics:
Jupiter has a mass of 1.898 × 10^27 kilograms, which is about 318 times the mass of Earth. It rotates on its axis once every 9 hours and 56 minutes, which makes it the fastest rotating planet in the solar system. Its surface temperature is about -145 degrees Celsius (-234 degrees Fahrenheit), which is much colder than Earth’s average temperature of 15 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit).
Atmosphere:
Jupiter’s atmosphere is the largest planetary atmosphere in the solar system, extending up to 5,000 kilometers (3,000 miles) above the planet’s surface. It is composed of about 90% hydrogen and 10% helium, with trace amounts of methane, ammonia, water vapor, and other compounds. The atmosphere also contains powerful storms, such as the Great Red Spot, which is a giant storm that has been raging for at least 350 years.
Magnetic Field:
Jupiter has a strong magnetic field that is generated by its rotating liquid metallic hydrogen core. The magnetic field is tilted at an angle of about 11 degrees to Jupiter’s axis of rotation and is about 20,000 times stronger than Earth’s magnetic field. It creates auroras near the planet’s poles and interacts with the solar wind to create intense radiation belts.
Role in the Solar System:
Jupiter’s large mass and strong gravitational field have significant effects on the rest of the solar system. It has helped to shape the orbits of the other planets, particularly the inner rocky planets, by deflecting asteroids and comets away from them. It also acts as a shield, protecting the inner solar system from potentially hazardous objects that could collide with Earth.
Future Missions:
Jupiter continues to be an object of study for scientists, and there are plans for future missions to explore the planet and its moons. These missions include the European Space Agency’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) and NASA’s Europa Clipper, which will study Jupiter’s moons Europa and Ganymede, respectively.
In conclusion, Jupiter is an awe-inspiring planet with many unique characteristics that continue to intrigue scientists and space enthusiasts alike. Its large size, powerful magnetic field, and vast atmosphere make it an important object of study in the solar system.
